Introduction
Importance of Comprehensive Biceps Training
The best bicep routine for mass , is a comprehensive biceps training is crucial for optimal biceps development as it targets all aspects of the biceps muscle, ensuring balanced growth and strength. To achieve this, it is essential to incorporate exercises that cover the three major functions of the biceps: elbow supination, elbow flexion, and shoulder flexion.
By including a variety of exercises that work different parts of the biceps strength curve, individuals can maximize muscle contraction and stimulate growth effectively.
Additionally, focusing on both the long and short head of the biceps, as well as the brachialis muscle, contributes to overall biceps development and width. Training frequency of 1-2 times per week with 3-5 exercises per session is recommended for optimal results.
Slow and controlled movements during bicep curls can enhance the mind-muscle connection, aiding in quicker bicep growth.
Ultimately, a well-rounded strength training program that targets all major muscle groups along with specific biceps training is key to achieving comprehensive biceps development.

Targeting Brachialis and Brachioradialis for Enhanced Development
Targeting the brachialis and brachioradialis muscles is essential for achieving enhanced development of the upper arm. The brachialis muscle, located in the upper arm, is a powerful flexor of the forearm and plays a significant role in elbow flexion, contributing to overall arm size and strength.
On the other hand, the brachioradialis muscle, which crosses the elbow joint and is situated near the forearm, also assists in elbow flexion movements.
To effectively target these muscles for enhanced development, exercises that specifically engage them should be incorporated into a comprehensive training routine. By focusing on movements that isolate and activate the brachialis and brachioradialis, individuals can promote balanced muscle growth in the upper arm region, leading to improved aesthetics and functional strength
Additionally, paying attention to these muscles can help address any imbalances between the long and short heads of the biceps, contributing to a more symmetrical and well-developed arm physique.
Incorporating exercises like hammer curls and forearm exercises can help target these muscles effectively, promoting overall arm development.
The Best Bicep Routine for Mass
Understanding Biceps Anatomy
Role of Biceps Brachii, Brachialis, and Brachioradialis
The biceps brachii, brachialis, and brachioradialis muscles play crucial roles in the movement and stabilization of the upper arm and forearm, each contributing uniquely to forearm flexion and other actions.
Biceps Brachii
The biceps brachii is a prominent muscle in the anterior compartment of the upper arm, consisting of two heads: the long head and the short head. The long head originates from the supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula, while the short head originates from the coracoid process of the scapula. Both heads insert into the radial tuberosity and the fascia of the forearm via the bicipital aponeurosis.
The primary functions of the biceps brachii include supination of the forearm, flexion at the elbow, and to a lesser extent, flexion at the shoulder. It is innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve and receives its blood supply from the brachial artery.
Brachialis
The brachialis muscle is located deep to the biceps brachii in the anterior compartment of the upper arm. It originates from the medial and lateral surfaces of the humerus shaft and inserts onto the ulnar tuberosity, just distal to the elbow joint.
Its primary function is flexion at the elbow, making it a powerful flexor of the forearm. The brachialis is innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve, with contributions from the radial nerve, and is supplied by the brachial and radial arteries.
Unlike the biceps brachii, the brachialis’ action is not affected by the position of the forearm (pronation or supination), making it the only pure flexor of the elbow joint.
Brachioradialis
The brachioradialis is a superficial muscle located on the posterior compartment of the forearm. It originates from the lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus and inserts at the styloid process of the radius.
The brachioradialis is responsible for flexion of the forearm, particularly when the forearm is in a mid-pronated position. It also assists in pronation and supination when the arm is fully pronated or supinated, respectively.
The muscle is innervated by the radial nerve (C5-C6) and receives blood supply from the radial recurrent artery, a branch of the radial artery.
The brachioradialis works in synergy with the biceps brachii and brachialis to flex the forearm at the elbow, especially during activities that require a semi-pronated position, such as hammering or rowing.
The biceps brachii, brachialis, and brachioradialis muscles are integral to the flexion and stabilization of the elbow and forearm. Each muscle has distinct origins, insertions, and functions that contribute to the complex movements of the upper limb.
The Only 3 Exercises You Need For Big Biceps (GET A HUGE PUMP!)
Addressing Imbalances for Symmetrical Growth
Addressing imbalances in muscle strength and symmetry is crucial for achieving symmetrical growth and preventing potential issues related to muscle imbalances. Muscle imbalances can lead to limited mobility, pain, an unbalanced appearance, and even instability, increasing the risk of injuries to joints, ligaments, tendons, bones, muscles, and connective tissue.
To promote symmetrical growth and address imbalances effectively, various strategies can be employed:
- Identifying Imbalances: Utilize methods like biometric testing or observation to identify muscle imbalances in the body. This can involve assessing strength deficiencies and size imbalances through targeted exercises or visual assessments.
- Corrective Exercises: Engage in exercises that target specific muscle groups to address weaknesses and imbalances. Incorporating single-limb exercises like single-leg calf raises or single-arm chest presses can help isolate and strengthen individual muscles to restore symmetry.
- Proper Form: Ensure that exercise form is correct by working with a fitness professional or using mirrors to monitor movements during workouts. Proper form is essential for targeting muscles effectively and avoiding further imbalances.
- Balanced Training: Include a mix of double-limb and single-limb exercises in your workout routine to promote overall symmetry. Pay attention to any differences between sides during single-limb activities and address imbalances promptly.
- Endurance Training: Evaluate muscular endurance to ensure balanced usage of muscles. Addressing endurance asymmetries can prevent postural issues or incorrect movement patterns that may lead to strain or pain.
- Flexibility Training: Incorporate flexibility exercises into your routine to maintain balanced flexibility across muscle groups. Asymmetries in flexibility can contribute to poor posture, reduced range of motion, and an increased risk of injury.
By implementing these strategies consistently and seeking guidance from fitness professionals when needed, individuals can work towards achieving symmetrical growth, reducing the risk of injuries, and optimizing overall physical performance.
The Science Behind Prioritization

Rationale for Initiating with Smaller Muscles
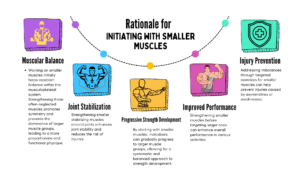
The rationale for initiating a workout routine by targeting smaller muscles before transitioning to larger muscles is based on the principles of muscular balance, joint stabilization, and injury prevention. By focusing on smaller muscles first, individuals can achieve several key benefits that contribute to overall fitness and performance:
- Muscular Balance: Working on smaller muscles initially helps establish balance within the musculoskeletal system. Strengthening these often-neglected muscles promotes symmetry and prevents the dominance of larger muscle groups, leading to a more proportionate and functional physique.
- Joint Stabilization: Strengthening smaller stabilizing muscles around joints enhances joint stability and reduces the risk of injuries. These muscles play a crucial role in supporting joint movements and maintaining proper alignment during physical activities, contributing to overall joint health.
- Progressive Strength Development: By starting with smaller muscles, individuals can gradually progress to larger muscle groups, allowing for a systematic and balanced approach to strength development. This progression helps build a solid foundation of strength and stability before moving on to more complex movements involving larger muscle groups.
- Improved Performance: Strengthening smaller muscles before targeting larger ones can enhance overall performance in various activities. A well-balanced musculature ensures optimal force transmission, movement efficiency, and coordination, which are essential for athletic performance and functional movements.
- Injury Prevention: Addressing imbalances through targeted exercises for smaller muscles can help prevent injuries caused by asymmetries or weaknesses. By identifying and correcting these imbalances early on, individuals reduce the risk of overuse injuries, strains, and joint issues that may arise from muscular imbalances.
Initiating a workout routine by prioritizing smaller muscles offers a strategic approach to building a strong foundation, promoting muscular balance, enhancing joint stability, improving performance, and reducing the risk of injuries. By focusing on these often-overlooked muscle groups first, individuals can lay the groundwork for sustainable progress in their fitness journey while safeguarding against potential imbalances and associated risks.
Maximizing Recruitment for Optimal Growth

To maximize bicep recruitment for optimal growth and develop mass effectively, a comprehensive bicep routine should focus on targeting both the long and short heads of the biceps. Here is a summary of the key points from the provided sources to create an effective bicep routine:
Key Points for an Effective Bicep Routine:
- Exercise Selection: Incorporate a variety of exercises that target different aspects of the biceps, such as full range of motion basics, supination function, peak contraction, and stretch. Examples include barbell curls, dumbbell twist curls, spider curls, and incline dumbbell curls.
- Volume: Aim for 2-4 weekly sessions dedicated to biceps training to optimize muscle growth. Experiment with different curl variations and intensity techniques to challenge the muscles effectively.
- Training Frequency: Consider training biceps directly 3-4 times per week during specialization phases to allow for more recovery and growth. Adjust volume based on your recovery capacity and muscle response.
- Combination with Back Training: While back exercises indirectly work the biceps, direct bicep training is essential for maximizing size. For individuals who train back extensively, additional direct bicep work may be necessary to achieve maximum growth.
- Isolation Exercises: Include exercises that isolate the biceps effectively, such as concentration curls and preacher curls, to target specific areas of the biceps and prevent cheating or swinging during movements.
- Focus on Form: Emphasize slow and controlled movements during exercises like preacher curls to maximize muscle activation, especially during the eccentric or lowering phase of the movement.
By incorporating a mix of exercises that target different aspects of the biceps, adjusting training volume based on individual response, and ensuring proper form during isolation exercises, you can create an effective bicep routine that maximizes recruitment for optimal growth and mass development.
Top Trainers Agree, These are the 10 Best Exercises for Building Bigger Arms
The Big Biceps Workout Routine
Warm-up and Preparation
The warm-up phase before physical activity is crucial for both mental and physical preparation. It serves as a critical period for performers to not only prepare their bodies but also to focus mentally on the upcoming challenge. A good warm-up involves various elements that contribute to optimal readiness for performance:
- Mental Preparation: During the warm-up, performers are given time to be quiet, socialize with teammates, and focus on the upcoming challenge. This helps in relaxation and mental readiness for the task ahead.
- Physical Aspects: The quality of the physical warm-up is essential for instilling confidence in performers that they are physically prepared. This phase includes activities that raise body temperature, heart rate, respiration rate, blood flow, and joint viscosity.
- Performance Goals: Discussions during the warm-up focus on performance goals rather than outcome goals. This helps performers concentrate on the process and tasks at hand rather than solely on the end result.
- Positive Self-Talk: Coaches play a vital role in encouraging positive self-talk among performers by framing discussions in a positive manner. This positive reinforcement can enhance confidence and mental preparedness.
- Warm-Up Models: Two primary warm-up models, the “RAMP” protocol by Dr. Ian Jeffreys and Mark Verstegen, emphasize a structured approach to warm-ups involving phases like Raise, Activate and Mobilize, and Potentiate or Performance. These models aim to fully prepare athletes both mentally and physically for competition or activity.
An effective warm-up routine combines mental preparation with physical readiness through activities that raise body temperature, promote blood flow, encourage positive self-talk, and focus on performance goals rather than outcomes. By incorporating these elements into the warm-up process, performers can optimize their readiness for the challenges ahead and enhance their overall performance potential.
Targeted Exercises for Explosive Growth
The best bicep routine for mass and explosive growth involves a combination of targeted exercises that focus on the biceps from various angles and with different levels of intensity. Here are key exercises recommended across the provided sources for maximizing bicep muscle development:
- Barbell Curls: Barbell curls are a staple exercise for building bigger arms as they activate multiple muscles in the upper arms. This exercise involves gripping a barbell with an underhand grip, standing straight, and curling the bar up toward your chest in an arc while keeping elbows close to your sides. Lower the weight slowly to engage the biceps fully.
- Dumbbell Preacher Curls: Dumbbell preacher curls are considered an isolating movement that focuses stress on the short head of the bicep, contributing to peak development and fullness in the muscle. This exercise involves holding a dumbbell with an underhand grip while locking the elbow firmly in place on a preacher bench and curling the weight upwards.
- Incline Hammer Curl: The incline hammer curl is an isolation exercise that targets the biceps with precision and aids in improving arm strength and shoulder stabilization. This exercise is performed by sitting on an incline bench, holding dumbbells with palms facing the body, moving arms upwards by bending elbows, and holding the contraction before returning to the initial position.
- Zottman Curl: The Zottman curl is effective for toning biceps and building stronger arms while also developing the forearms. This exercise involves standing straight, holding dumbbells with palms facing the body, moving weights upwards while keeping upper arms stationary, rotating arms at the top of the motion, and returning to the initial position.
- Overhead Cable Curl: The overhead cable curl is a cable exercise that tones and strengthens the biceps with accuracy while improving stabilizing muscles for a complete upper body workout. This exercise is performed by standing between two high pulleys, setting appropriate resistance, pulling weights by squeezing biceps until forearms nearly touch shoulders, and returning to the initial position.
Bicep Routine for Explosive Growth:
- Barbell Curls:
- Sets: 4 sets
- Reps: 8-10 reps per set
- Execution: Grip the barbell with an underhand grip around shoulder-width apart. Keep your chest up and curl the barbell towards your chin while maintaining proper form.
- Dumbbell Preacher Curls:
- Sets: 3 sets
- Reps: 10-12 reps per set
- Execution: Sit on a preacher bench and curl the dumbbells upwards towards your shoulders, focusing on the contraction of the biceps at the top of the movement.
- Incline Hammer Curl:
- Sets: 3 sets
- Reps: 12-15 reps per set
- Execution: Perform hammer curls standing with feet shoulder-width apart, palms facing inward. Curl the weights upward and inwards towards your chest for overall arm thickness.
- Zottman Curl:
- Sets: 3 sets
- Reps: 10-12 reps per set
- Execution: Stand with feet shoulder-width apart, perform a regular curl with palms facing up, then rotate your wrists at the top of the movement to face down before lowering the weight.
- Overhead Cable Curl:
- Sets: 3 sets
- Reps: 12-15 reps per set
- Execution: Sit at a cable machine with upper arms on the pad. Grasp a cable bar with an underhand grip and curl the bar up towards your chest to isolate the long head of the biceps.
Addressing Training Scenarios
Workout 1: Biceps Isolation
When addressing training scenarios for a bicep routine focused on mass gain, it’s essential to consider specific workout plans that target biceps isolation effectively. Here is a structured workout plan for Biceps Isolation that can aid in maximizing muscle growth:
Workout 1: Biceps Isolation
- Barbell Cheat Curls:
- Sets: 3 sets to failure
- Execution: Perform as a drop set with Barbell Drag Curls. This exercise targets the biceps and forearms, allowing you to lift heavier weights and stimulate muscle growth effectively.
- Barbell Drag Curls:
- Sets: To failure
- Execution: Focus on hitting all three functions of the biceps with overload. This exercise emphasizes the full range of motion for the biceps, promoting muscle development and strength.
- Weighted Chin-Ups:
- Sets: 3 sets to failure
- Execution: Perform as a drop set with Peak Contraction Chin Curls. Weighted chin-ups are excellent for building strength in the biceps and back muscles, contributing to overall arm development.
- Peak Contraction Chin Curls:
- Sets: To failure
- Execution: This exercise targets the peak contraction of the biceps, enhancing muscle definition and promoting growth in specific areas of the biceps.
- Banded Dumbbell Curls:
- Sets: 3 sets to failure
- Execution: Incorporate resistance bands for added intensity and focus on achieving muscle fatigue to stimulate hypertrophy effectively.
- Dumbbell Incline Curls:
- Sets: 2 sets to failure (Stretch Reflex)
- Execution: Perform incline curls to target the long head of the biceps and emphasize the stretch reflex, enhancing muscle engagement and growth potential.
- Dumbbell Curl Trifecta:
- Sets: 2 sets (Alternate positions for a total of 8 reps in each position, each arm)
- Execution: Alternate between different positions to target various angles of the biceps, ensuring comprehensive muscle stimulation and growth.
This workout plan incorporates a variety of exercises that isolate the biceps effectively, focusing on different aspects of muscle development such as strength, peak contraction, and full range of motion. By following this structured routine with appropriate sets and reps, individuals can optimize their bicep training for mass gain and overall muscle growth.

Workout 2: Incorporating Biceps Training with Other Body Parts
Incorporating biceps training effectively within a comprehensive workout routine that targets multiple body parts is essential for balanced muscle development. When structuring a workout that includes biceps training along with other muscle groups, it is crucial to ensure proper sequencing and balance to optimize muscle growth and overall strength. Here is a suggested workout scenario that integrates biceps training with other body parts:
Workout 2: Incorporating Biceps Training with Other Body Parts
- Warm-up:
- Begin with a general warm-up routine to prepare your body for the workout.
- Primary Muscle Groups:
- Chest and Triceps:
- Perform compound exercises like bench press, incline bench press, or push-ups to target the chest and triceps effectively.
- Chest and Triceps:
- Secondary Muscle Groups:
- Back and Biceps:
- Engage in exercises such as bent-over rows, pull-ups, or lat pulldowns to work the back muscles along with the biceps.
- Back and Biceps:
- Isolation Exercises:
- Biceps:
- Incorporate targeted biceps exercises like standing barbell curls, alternating dumbbell curls, or hammer curls to focus specifically on bicep development.
- Biceps:
- Superset or Circuit Training:
- To maximize efficiency and intensity, consider incorporating supersets or circuit training that alternates between exercises targeting different muscle groups without rest in between sets.
- Cool Down and Stretching:
- Conclude the workout with a cool-down period and stretching routine to aid in muscle recovery and flexibility.
By structuring your workout routine in this manner, you can effectively target multiple muscle groups while ensuring that biceps training is integrated strategically within the overall workout plan. This approach allows for balanced muscle development, efficient use of time, and optimal results in terms of strength and mass gains across various body parts.
Strategies for Symmetrical Growth (Best bicep routine for mass)
Identifying and Addressing Biceps Imbalance
When aiming to develop biceps for mass effectively, it is crucial to focus not only on muscle growth but also on achieving symmetry and addressing any imbalances.
Here are some strategies derived from the provided sources to promote symmetrical growth and address biceps imbalances:
| Symmetrical Growth | |
|---|---|
| Overall Development: | Building a symmetrical physique involves focusing on overall body development rather than just isolated muscle groups like the biceps. |
| Continuous Process | Achieving symmetry is an ongoing process that requires attention to weak points and avoiding overwhelming strong points to prevent imbalances. |
| Left-Right Balance | Symmetry extends beyond top-to-bottom balance; it also involves ensuring that one side of the body is not noticeably larger or smaller than the other. |
| Identifying and Addressing Imbalances | |
| Dominant Side | Most individuals have a dominant side, leading to potential size differences between the dominant and non-dominant sides. Addressing this imbalance is crucial for symmetrical development. |
| Training Log: | Keeping a training log helps track progress and identify areas that need improvement, allowing for adjustments to maintain balance and symmetry in muscle development. |
| Balancing Workouts | While targeting the biceps is important, neglecting other muscle groups can lead to imbalances. Incorporating exercises for other muscle groups like triceps, shoulders, and back is essential for overall symmetry. |
By incorporating these strategies into your bicep routine for mass, you can not only promote balanced muscle growth but also work towards achieving a symmetrical physique by addressing any existing imbalances effectively. Remember that a well-rounded approach to training, focusing on overall body development and symmetry, is key to attaining optimal results in muscle mass and aesthetics.
Volume and Frequency Adjustments for Equal Development
To ensure symmetrical growth and equal development of your biceps, it is essential to incorporate strategies that focus on balancing muscle development and addressing any existing imbalances. Here are some key strategies derived from the provided sources to promote symmetrical growth and adjust volume and frequency for equal biceps development:
- Balancing Muscle Development:
- Unilateral vs. Bilateral Exercises: Incorporate unilateral arm exercises alongside bilateral exercises to ensure proper balance and prevent shifting more weight to the stronger side during workouts.
- Combining Exercises: Pair unilateral exercises that target each side individually with bilateral exercises to correct muscle imbalances effectively.
- Proper Form: Maintain proper form during exercises to prevent imbalances or exacerbating existing ones. Seek guidance from a personal trainer or physical therapist to ensure correct exercise execution.
- Volume and Frequency Adjustments:
- Training Log: Keep a training log to track progress, identify areas for improvement, and adjust sets, reps, and weights accordingly for continuous growth and balanced development.
- Progressive Overload: Gradually increase the intensity of your workouts by adding more weight, sets, reps, or advanced exercise variations to stimulate muscle growth and avoid plateaus.
- Training Frequency: Aim to train the biceps 2-3 times per week with at least 48 hours of rest between sessions to provide adequate stimulus for growth while allowing for proper recovery.
- Balanced Workouts: Incorporate compound exercises targeting multiple muscle groups like rows, pull-ups, and bench presses to ensure overall muscle development and symmetry alongside biceps training.
By implementing these strategies in your bicep routine for mass, you can promote symmetrical growth, address imbalances effectively, and adjust volume and frequency to achieve equal development of your biceps while maintaining overall muscle balance and proportion

Ensuring Progressive Overload
Importance of Regular Assessment and Modification
the best bicep routine for mass involves ensuring progressive overload and the importance of regular assessment and modification to optimize muscle growth. Here are key insights from the sources:
- Progressive Overload:
- Weighted Chin Up: Incorporating exercises like the Weighted Chin Up allows for progressive overload by adding weight over time to build arm strength and size effectively.
- Resistance Bands: Using resistance bands in exercises like the Banded Dumbbell Curl helps create constant tension and increase peak muscular tension throughout the entire range of motion, promoting progressive overload.
- Barbell Curls: Exercises like Barbell Curls and Hammer Curls allow for heavy lifting and progressive overload, essential for stimulating muscle growth and strength gains.
- Variety in Exercises: Including a variety of exercises such as Dumbbell Curls, Cheat Curls, Hammer Curls, and Concentration Curls helps challenge the biceps in different ways to maximize hypertrophy and muscle growth.
- Regular Assessment and Modification:
- Training Log: Keeping a training log helps track progress, identify areas for improvement, and adjust sets, reps, and weights to ensure continuous growth and balanced development.
- Quality Over Quantity: Emphasizing proper form and technique over simply increasing sets or reps is crucial for effective bicep workouts. Quality execution of exercises is key to maximizing results.
- Personal Trainer Guidance: Working with a personal trainer can help assess your ability, set goals, and create a customized workout plan tailored to your needs for optimal results in muscle growth.
- Nutrition and Recovery: Adequate nutrition, particularly protein intake, along with sufficient rest and recovery play a vital role in supporting muscle growth. Balancing workouts with proper nutrition and rest is essential for optimal results.
By incorporating progressive overload techniques into your bicep routine while regularly assessing your progress and making necessary modifications to your workout plan, you can effectively promote muscle growth, strength gains, and overall development of your biceps. Remember that consistency, proper form, variety in exercises, and attention to recovery are key factors in achieving desired results in bicep mass building.

Fine-tuning Intensity and Volume for Long-term Progress
the best bicep routine for mass involves ensuring progressive overload and fine-tuning intensity and volume for long-term progress. Here are key insights from the sources to help optimize your bicep routine:
- Progressive Overload:
- Importance: Progressive overload, achieved by gradually increasing the weight lifted over time, is crucial for continuous muscle growth and strength gains in your biceps.
- Variety of Exercises: Incorporating a variety of exercises like barbell curls, dumbbell curls, and cable curls allows for different stimuli and challenges to promote progressive overload effectively.
- Proper Form: Maintaining proper form during exercises is essential to target the biceps effectively and prevent injury while progressively overloading the muscles.
- Fine-tuning Intensity and Volume:
- Exercise Selection: Choose a mix of exercises that target both the long head and short head of the biceps to ensure balanced development and maximize muscle growth potential.
- Training Frequency: While there are no strict rules on how often to train biceps, consider factors like recovery capacity, overall fitness level, and goals when determining training frequency. Starting with training biceps twice a week can be a good approach for beginners.
- Nutrition and Recovery: Adequate nutrition, particularly protein intake, along with proper rest and recovery play a significant role in supporting muscle growth. Ensure you have a balanced diet and allow sufficient time for recovery between workouts to optimize progress.
By incorporating progressive overload techniques into your bicep routine, focusing on a variety of exercises that target different parts of the biceps, and fine-tuning intensity and volume based on your fitness level and goals, you can effectively promote muscle growth, strength gains, and long-term progress in developing your biceps. Remember to prioritize proper form, adequate nutrition, rest, and recovery to support your muscle-building efforts effectively.
Conclusion
Advanced Strength Training Programs & Strength Training Programs
| Advanced Strength Training Programs. | Strength Training Programs. |
|---|---|
| Dynamic Effort Method | 4+2 Method |
| Ultimate Hypertrophy Training | Functional Strength Training |
| StrongLifts 5×5 | Strength Gym Training |
| 5-Day Dynamic Weightlifting Program | Bear Workout |
FAQs on the Best Bicep Routine for Mass
Q)What is the best bicep routine for mass?
The best bicep routine for mass typically includes a combination of compound and isolation exercises that target the biceps from various angles. Exercises like barbell curls, dumbbell curls, hammer curls, and cable curls are commonly incorporated into mass-building routines.
Q) How many times a week should I train my biceps for mass?
Training frequency can vary based on individual factors such as recovery ability and overall training volume. However, most people find success with training their biceps 2-3 times per week with at least 48 hours of rest between sessions to allow for adequate recovery.
Q) How many sets and reps should I do for bicep mass?
For mass-building purposes, aim for moderate to high volume with a rep range of 8-12 reps per set. Perform 3-5 sets of each exercise, focusing on gradually increasing the weight lifted over time to promote muscle growth through progressive overload.
Q) Should I incorporate both compound and isolation exercises into my bicep routine for mass?
Yes, incorporating both compound and isolation exercises into your bicep routine can be beneficial for mass gain. Compound exercises like barbell curls or weighted chin-ups allow you to lift heavier weights and target multiple muscle groups, while isolation exercises like dumbbell curls or cable curls focus specifically on the biceps for maximum muscle activation.
Q) How important is proper form when performing bicep exercises for mass?
Proper form is crucial when performing bicep exercises to maximize muscle engagement and prevent injury. Focus on controlled movements, avoid swinging or using momentum to lift weights, and ensure a full range of motion with each repetition for optimal results.
Q) Should I train my biceps separately or with other muscle groups?
Both approaches can be effective for mass gain, and the choice depends on individual preferences and training goals. Some people prefer to dedicate a separate day to biceps training to focus solely on arm development, while others prefer to incorporate biceps exercises into their overall upper body or split routines.
Q) How long should my bicep workouts be for mass gain?
Bicep workouts for mass gain typically last anywhere from 45 minutes to an hour, including warm-up and cool-down periods. Focus on efficiency and intensity during your workouts, prioritizing quality over quantity to stimulate muscle growth effectively.
Q) Is it necessary to change my bicep routine frequently to continue making gains?
While some variation in your bicep routine can be beneficial to prevent plateaus and keep workouts engaging, it’s not necessary to change your routine frequently if you’re still seeing progress. Focus on progressive overload by gradually increasing the weight lifted or making small adjustments to sets, reps, or exercise selection over time.




